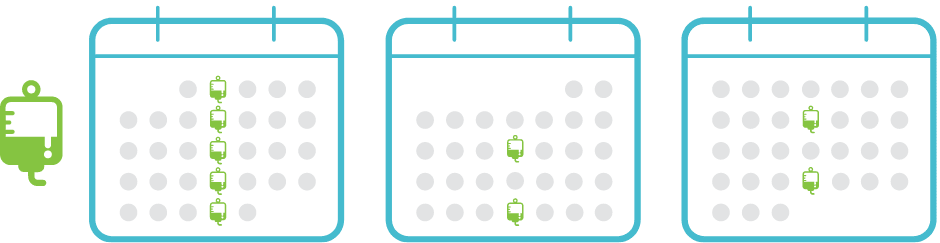
POTELIGEO Dosing frequency1

Administer once-weekly loading dose for the first 5 infusions, then once every 2 weeks thereafter
DOSING SCHEDULE
Recommended premedication for prophylaxis1:
First dose
Administer premedication with diphenhydramine and acetaminophen prior to the first POTELIGEO infusion
If infusion reaction occurs
Prior to subsequent infusions, administer diphenhydramine and acetaminophen
Infusion reaction may require dosing adjustments1:
- 33% of patients (61/184) experienced an infusion reaction
- 2% (4/184) were >Grade 3
- ~90% occurred during or shortly after first infusion
Missed doses
- If the dose is administered within 2 days of these scheduled doses, continue original schedule
- If the scheduled dose is missed by more than 2 days, administer the missed dose as soon as possible and resume dosing schedule
No dosing changes required in special populations1
No clinically significant changes in pharmacokinetics based on:
- Age (range 22-101 years)
- Renal impairment (mild, moderate, or severe)
- Disease subtype (MF or SS)
- CCR4 expression level
- ECOG Performance Status
- Sex
- Ethnicity
No differences in efficacy between older and younger patients:
- <65 years of age
- ≥65 years of age
Dosing modifications for dermatologic toxicity1,a
Dosing modifications for infusion reactions1,c
Common signs of infusion reactions
chills | nausea | fever | tachycardia | rigors | headache | vomiting
- aGrades are based on CTCAE v.5.0.
- bFor suspected SJS or TEN, stop POTELIGEO; do not resume treatment unless SJS or TEN has been excluded and the cutaneous reaction has been resolved to ≤Grade 1.1
- cLess than 1% of all POTELIGEO-treated patients in clinical trials experienced Grade 4 skin adverse reactions; SJS occurred in <1% of patients.1
- CCR4=C-C chemokine receptor type 4; ECOG=Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; MF=Mycosis Fungoides; NSAID=nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug; SJS=Stevens-Johnson syndrome; SS=Sézary Syndrome; TEN=toxic epidermal necrolysis
See how to get started with POTELIGEO
- POTELIGEO [package insert]. Kyowa Kirin Inc., Princeton, NJ USA.



