Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (CTCLs) are a heterogenous group of T-cell lymphomas that present in the skin1,2
Mycosis Fungoides, the most common subtype of CTCL, may be indolent with skin-only symptoms but can involve blood, lymph nodes, and viscera1,3-5
Examples of patches, plaques, and tumors in Mycosis Fungoides (MF).
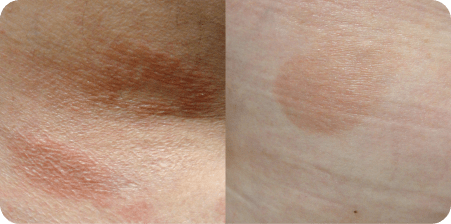
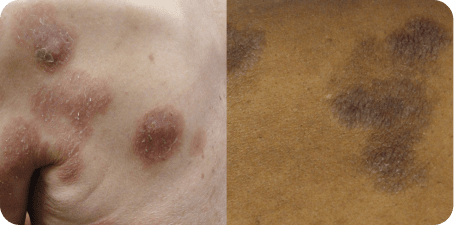
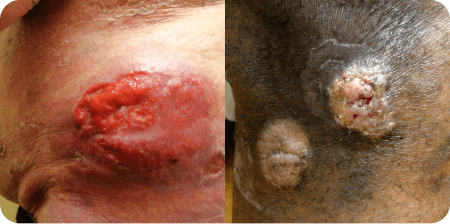
aPhotos courtesy of Oleg Akilov, MD, PhD.
CTCL Expert Perspectives: Patient Identification
Andrei Shustov, MD discusses identifying therapy-refractive patients, how blood involvement can impact treatment selection, how clinical practice guidelines help shape decisions, and appropriate patient types for treatment with POTELIGEO based on data from the phase 3 MAVORIC trial.
Explore why POTELIGEO is a preferred treatment option
- Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Primary Cutaneous Lymphomas V.1.2025. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2024. All rights reserved. Accessed February 11, 2025. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org.
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105(10):3768-3785.
- Amorim GM, Niemeyer-Corbellini JP, Quintella DC, Cuzzi T, Ramos-E-Silva M. Clinical and epidemiological profile of patients with early stage mycosis fungoides. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93(4):546-552.
- Scarisbrick JJ, Quaglino P, Prince HM, et al. The PROCLIPI international registry of early-stage mycosis fungoides identifies substantial diagnostic delay in most patients. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181(2):350-357.
- Latzka J, Assaf C, Bagot M, et al. EORTC consensus recommendations for the treatment of mycosis fungoides/Sézary syndrome - Update 2023. Eur J Cancer. 2023;195:113343.
